History
1850s–1890s – Stockmann is established
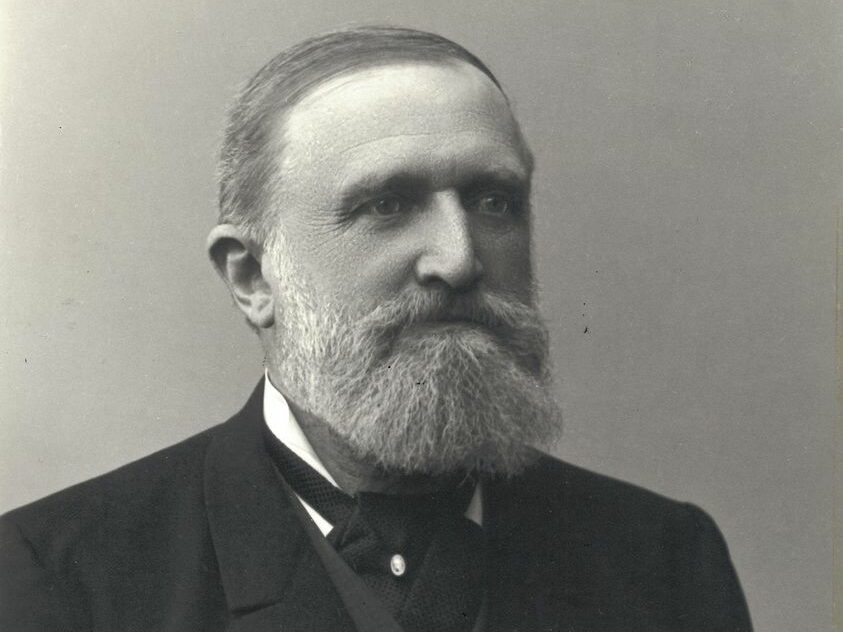
Stockmann was established by Heinrich Georg Franz Stockmann (1825–1906), who moved to Finland from Lübeck and took over the Nuutajärvi Glassworks store in Helsinki on 1 February 1862.
In 1880, Stockmann opened a ‘continental department store’, the type of which had never been seen in Finland before, in a building on Senate Square, which is now known as the Kiseleff bazaar.
In 1897, Stockmann opened his first branch in the Kallio district of Helsinki, which operated until 1960.


1900s–1920s – Stockmann department store is opened on Aleksanterinkatu
In 1902, the one-man business became a limited company, G.F. Stockmann Aktiebolag, when the shareholder base of the company owned by Stockmann and his sons Karl and Frans expanded.
Stockmann’s long history in Finnish design began in 1919 with the acquisition of the Keravan Puusepäntehdas carpentry factory, which operated until 1985.
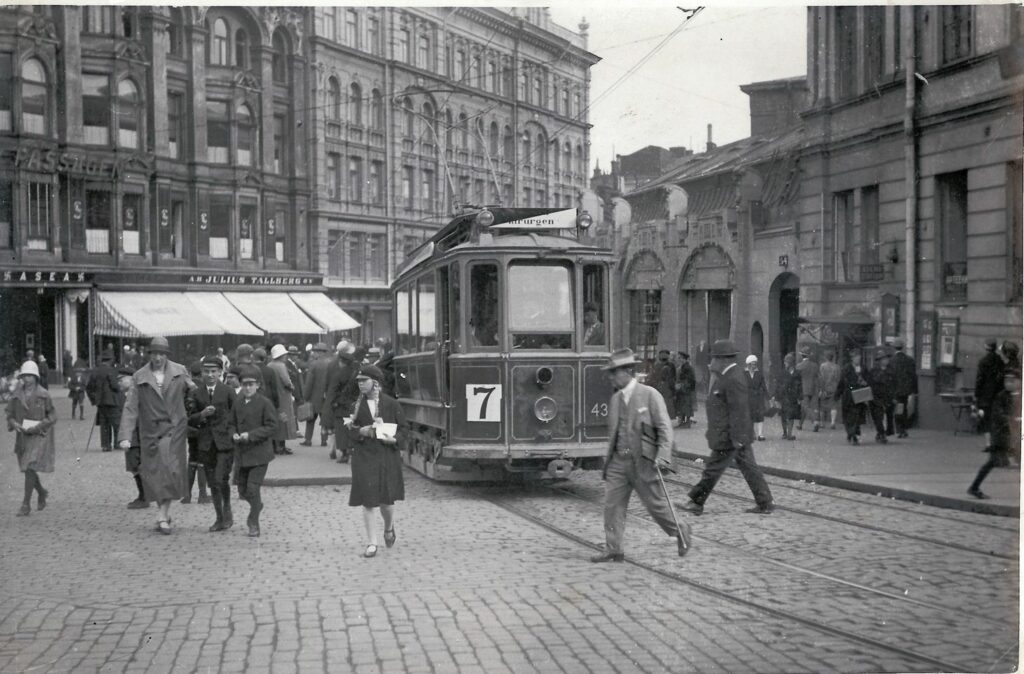
The Stockmann department store has been located on the iconic corner of Pohjoisesplanadi, Aleksanterinkatu and Keskuskatu in Helsinki since 1922. A two-storey section, designed by architect Sigurd Frosterus, was initially built on the corner, but this was extended into a four-storey department store that was inaugurated by President Lauri Kristian Relander in 1926.
1930s–1950s – Lindex is established and Stockmann acquires the Academic Bookstore
In 1930, Stockmann took a big step forward with the acquisition of the Academic Bookstore. In the same year, Stockmann’s new department store in Helsinki was completed, and people were amazed by the escalators, revolving doors, grand atrium and soda fountain.
Investors have been able to buy Stockmann’s shares on the stock exchange since 1942.
Finland was in the grips of the Winter War and the Continuation War. Two bombs struck Stockmann’s department store during heavy bombardments in February 1944. After the war ended it was difficult to get well-trained personnel, so Stockmann set up its own school for sales assistants in 1946. A kindergarten for the children of Stockmann personnel was also set up, as there was no municipal day care for children in Finland at that time. The kindergarten operated until 1977.
Finland’s first ever television transmission was broadcast by cable in the Stockmann department store in 1950.
Lindex’s history dates back to 1954, when Swedes Ingemar Boman and Bengt Rosell established a lingerie store called Fynd in Alingsås, Sweden. Shortly afterwards, the company bought a company in Gothenburg called Lindex, which gave its name to the future stores.
Stockmann’s first local department store was opened in Tampere in 1957.


1960s–1980s – Lindex and Stockmann expand
In the 1960s, Lindex’s product range expanded from underwear to womenswear and the first Lindex store was opened in Norway. In the 1970s, Lindex continued to expand its operations in Sweden and Norway. The womenswear range was diversified and kidswear was introduced into the Lindex offering. Lindex’s expansion culminated in the 1980s and almost all textile production was moved abroad. Lindex entered new markets, such as Denmark, the UK and Finland, but by the end of the 1980s the business was geographically concentrated in Sweden, Norway and Finland.
Stockmann continued to grow, acquiring the retailer Sesto in 1962, the clothing store Seppälä in 1988, and Hobby Hall, which is still in operation today, in 1985.
Stockmann also opened more local department stores, such as the Pietarsaari department store (1967-1982) and the Kouvola department store (1976-1982). The Tapiola department store, opened in 1981, and the Turku department store, opened in 1982, are both still in operation.
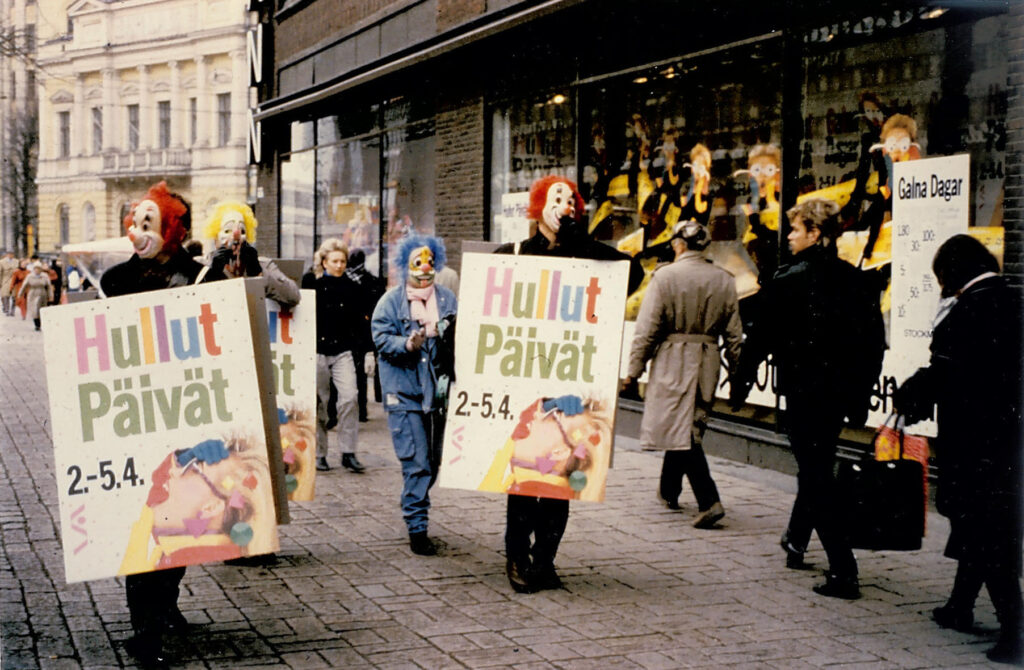
The most famous of the events and campaigns organised in Stockmann department stores is the Crazy Days event, and the first Crazy Days was held in April 1986.
In 1986, Stockmann pioneered modern loyal customer marketing. Another new feature was the loyal customer cash card, which was introduced in Finland for the first time.
1990s – Stockmann and Lindex become international
Stockmann launched operations outside Finland just before the 1990s when a store was opened in Russia. Stockmann’s first department store in Russia was opened in Moscow in 1998.
In 1992, Stockmann also expanded its operations in Finland when its department store in Helsinki’s Itäkeskus shopping centre opened for business.
Stockmann expanded its operations to Estonia by opening a clothing and household appliances store in 1993 and a department store in 1996, both in Tallinn.
Lindex opened its first production coordination office in Hong Kong in 1993, launching its systematic work to ensure a responsible supply chain began. In the late 1990s, Lindex acquired Fix, a brand specialising in children’s clothing.
The Group’s current name, Stockmann Oyj Abp, (Stockmann plc in English) was approved by the Annual General Meeting in 1998.
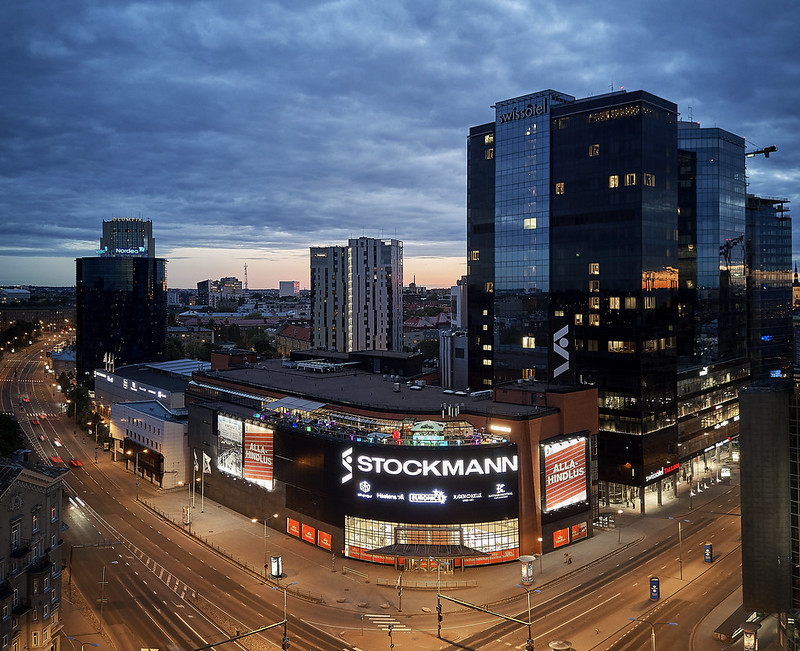


2000s – Stockmann acquires Lindex
Lindex expanded its operations significantly in Eastern Europe in the 2000s and opened stores in the Baltic countries and the Czech Republic.
Hobby Hall Online, the online store of Hobby Hall, owned by Stockmann, was launched in 2000 and quickly became Finland’s leading e-commerce site for consumers.
In 2001, Stockmann opened a new full-scale department store in the centre of Oulu.
In 2003, Stockmann opened a department store in the centre of Riga in Latvia, and expanded its department store in Tallinn into the largest department store in the Baltics. Stockmann also opened several department stores in Russia, where it had at most seven department stores.
In 2005, Stockmann opened its newest department store in the Jumbo shopping centre in Vantaa.
An important year in Stockmann’s history was 2007 as the company acquired Lindex, a Swedish company that is one of the leading fashion chains in Northern Europe.
In 2008, Lindex opened a store in St Petersburg, Russia, and in 2009 in Moscow and in Slovakia.
2010s – Decade of changes
In January 2011, Lindex launched its lindex.com online store, which now operates in 34 countries, and it continued to strengthen and consolidate its position in Central Europe in the 2010s.
In the 2010s the Stockmann Group’s decade was characterised by restructuring and divestments of selected Group companies. In 2015, Stockmann sold Seppälä to the company’s CEO Eveliina Melentjeff and her husband Timo Melentjeff. The Academic Bookshop was sold to the Bonnier Books AB media company. Today, the Academic Bookstore has four stores in department stores in Finland – including a store in Stockmann’s Book Building, which was designed by Alvar Aalto and opened in 1969.
In 2016, Stockmann divested Hobby Hall, which had evolved from a mail order business that was a subsidiary of Stockmann to Finland’s leading consumer e-commerce platform, which is still in operation today. Hobby Hall’s business operations were transferred to the Finnish SGN Group.
All Stockmann’s Russian department stores were sold to Reviva Holdings Limited in 2016 and the Nevsky Centre shopping centre in St Petersburg was sold to PPF Real Estate in 2019, thus ending Stockmann’s business operations in Russia. However, Reviva has a licence agreement to use the Stockmann brand name in Russia for the period 2019–2028.
In 2017, Stockmann sold its Delicatessen business operations in Finland to S Group’s regional cooperatives.
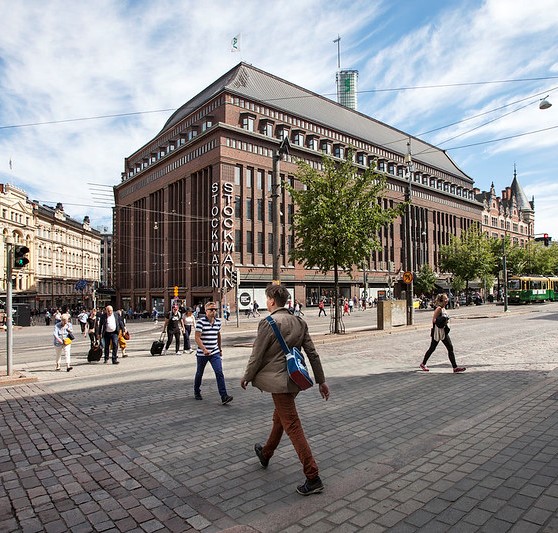


Years 2020–2022 – the pandemic stopped the world
In 2020, the corona pandemic halted both production and logistics chains worldwide, prevented the free movement of people also affected the profitability of Stockmann’s department store business. In the same year, the Stockmann division applied for corporate restructuring. Group subsidiaries, including the Stockmann department stores in the Baltics and Lindex, were not in scope of the restructuring proceedings.
In 2021, Stockmann’s department store properties in Tallinn and Riga were sold to the Estonian company Viru Keemia Grupp, and in March 2022, the department store property in the centre of Helsinki was sold to the Finnish company Keva. However, Stockmann continued its department store operations in all its current locations as a tenant.
In 2022, Stockmann turned 160 years old. Stockmann, which has grown into a significant brand and fashion department store icon in Finland and the Baltics, has had to renew itself over the years and adapt to the demands of the times.
Years 2023–2024 – strategic assessment and name change
In 2023, Stockmann plc’s Board of Directors decided to initiate a strategic assessment to crystallise shareholder value by refocusing the Group’s business on Lindex. The name of Stockmann Group’s parent company Stockmann plc was changed to Lindex Group plc in 2024. Lindex has had a fundamental role in improving the performance of the Group over the years. The name change of the parent company did not impact the Stockmann department stores iconic brand nor the names of Stockmann’s department stores or online store.
As part of the investigation of strategic alternatives, Lindex Group evaluates the best environment for developing the Stockmann’s department stores business. These options will include increasing the business’ independence within the Group, considering possible ownership changes or strategic partnerships, or continuing under the current structure. The strategic assessment doesn’t have any immediate impact on the Stockmann Department Stores’ brand or its daily business operations, which continues with full commitment in their ordinary course.

The Group today
Today, in addition to the online store stockmann.com, the Stockmann division has a total of six department stores in Finland – in the centre of Helsinki and the Itis shopping centre in Helsinki, in Tampere, in Tapiola in Espoo, in the centre of Turku and in the Jumbo shopping centre in Vantaa. In the Baltic countries, the department stores are located in Tallinn in Estonia and Riga in Latvia.
Stockmann offers a varied, high-quality and curated selection of fashion, beauty and home products for those seeking enrichment of their daily lives and special occasions. Stockmann inspires its customers to make sustainable and responsible choices.
In the 2000s, Lindex has grown into one of Europe’s leading fashion companies, with more than 440 stores in 17 countries. In addition, the lindex.com online store operates in 34 countries and Lindex products are sold online worldwide through third-party platforms.
Lindex’s business idea is to offer inspiring and affordable fashion to fashion-conscious women who take responsibility seriously. Lindex’s sustainability promise for future generations is built around empowering women, respecting the planet and ensuring human rights.
Get to know lindex And stockmann divisions
Lindex
Lindex is one of Europe’s leading fashion companies. The company was founded in 1954 in Alingås, Sweden. Lindex has around 430 stores in 18 countries, an online store that operates in 34 countries and online sales worldwide through third-party platforms.
Stockmann
Stockmann is a multichannel retail company that focuses on a range of fashion, beauty and home products for daily life and special occasions. Stockmann has a total of eight department stores in Finland and the Baltic countries and an online store.
 2025 . All rights reserved.
2025 . All rights reserved.